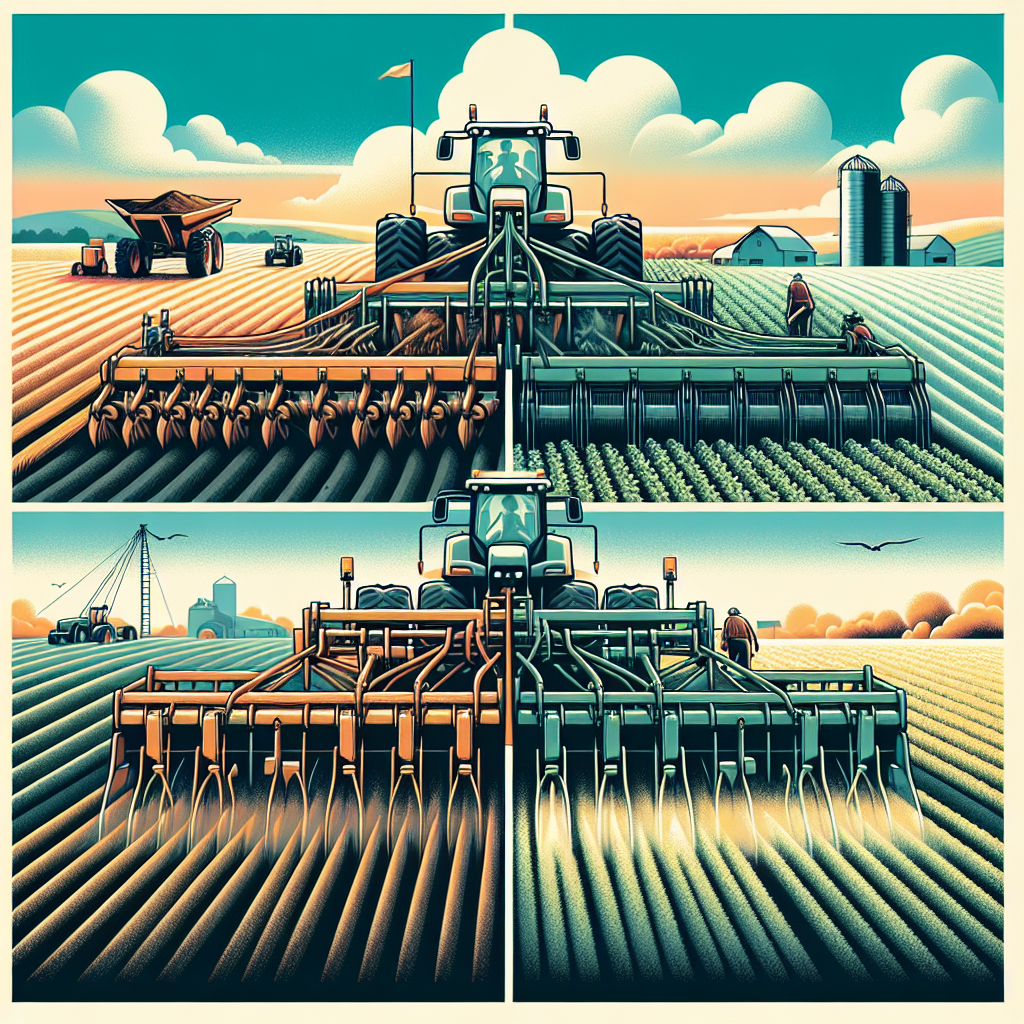
Choosing the right tillage method for your farm can significantly impact soil health, crop yield, and overall farm productivity. In this article, we will explore the differences between vertical tillage and conventional plowing, providing you with the insights needed to make an informed decision for your agricultural practices.
Understanding Vertical Tillage
Vertical tillage is a modern farming technique that involves the use of specialized equipment to cut through soil vertically. This method aims to manage crop residue, improve soil structure, and enhance water infiltration without causing significant soil disturbance. Unlike conventional plowing, which turns the soil over, vertical tillage maintains the soil’s natural layers, promoting better root growth and reducing erosion.
Benefits of Vertical Tillage
One of the primary advantages of vertical tillage is its ability to manage crop residue effectively. By cutting through residue and incorporating it into the soil, vertical tillage helps decompose organic matter more efficiently, enriching the soil with nutrients. Additionally, this method improves soil aeration and water infiltration, which are crucial for healthy root development and overall plant growth.
Another significant benefit of vertical tillage is its minimal soil disturbance. Unlike conventional plowing, which can disrupt soil structure and lead to erosion, vertical tillage preserves the soil’s natural layers. This preservation helps maintain soil health, reduces compaction, and promotes better water retention. As a result, crops can access nutrients and moisture more effectively, leading to higher yields.
Challenges of Vertical Tillage
Despite its numerous benefits, vertical tillage also presents some challenges. One of the main drawbacks is the initial cost of equipment. Vertical tillage implements can be expensive, and farmers may need to invest in new machinery or modify existing equipment to adopt this method. Additionally, vertical tillage may not be suitable for all soil types or farming conditions. For instance, heavy clay soils or fields with excessive residue may require more intensive management practices.
Conventional Plowing: A Traditional Approach
Conventional plowing, also known as moldboard plowing, is a traditional tillage method that involves turning the soil over to bury crop residue and prepare the seedbed. This technique has been used for centuries and remains popular among many farmers due to its effectiveness in weed control and soil preparation.
Benefits of Conventional Plowing
One of the main advantages of conventional plowing is its ability to control weeds effectively. By burying weed seeds and residue deep into the soil, plowing reduces the likelihood of weed growth, providing a cleaner seedbed for planting. Additionally, conventional plowing can help break up compacted soil layers, improving root penetration and nutrient uptake.
Conventional plowing also facilitates the incorporation of organic matter into the soil. By turning the soil over, plowing helps mix crop residue and other organic materials, enhancing soil fertility and structure. This process can lead to improved soil health and increased crop yields over time.
Challenges of Conventional Plowing
Despite its benefits, conventional plowing has several drawbacks. One of the most significant challenges is soil erosion. Turning the soil over exposes it to wind and water erosion, which can lead to the loss of valuable topsoil and nutrients. This erosion can negatively impact soil health and reduce long-term productivity.
Another challenge of conventional plowing is soil compaction. Repeated plowing can create a hardpan layer beneath the surface, restricting root growth and water infiltration. This compaction can lead to poor crop performance and reduced yields. Additionally, conventional plowing can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, requiring significant energy and resources.
Comparing Vertical Tillage and Conventional Plowing
When deciding between vertical tillage and conventional plowing, it’s essential to consider the specific needs and conditions of your farm. Both methods have their advantages and challenges, and the best choice will depend on factors such as soil type, crop rotation, and overall farm management goals.
Soil Health and Structure
Vertical tillage is generally better for maintaining soil health and structure. By minimizing soil disturbance, this method helps preserve the natural layers of the soil, promoting better water retention and root growth. In contrast, conventional plowing can disrupt soil structure and lead to erosion and compaction, which can negatively impact long-term soil health.
Weed Control and Seedbed Preparation
Conventional plowing is often more effective for weed control and seedbed preparation. By burying weed seeds and residue, plowing creates a cleaner seedbed, reducing competition for nutrients and water. However, vertical tillage can also manage residue effectively, and with proper management practices, it can provide adequate weed control.
Cost and Labor Considerations
Cost and labor are important factors to consider when choosing a tillage method. Vertical tillage equipment can be expensive, and the initial investment may be a barrier for some farmers. However, vertical tillage is generally less labor-intensive and can save time and resources in the long run. Conventional plowing, while potentially more affordable in terms of equipment, can be labor-intensive and require more energy and resources.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Farm
Ultimately, the decision between vertical tillage and conventional plowing will depend on your farm’s specific needs and conditions. Vertical tillage offers numerous benefits for soil health and structure, while conventional plowing provides effective weed control and seedbed preparation. By carefully considering the advantages and challenges of each method, you can make an informed decision that will enhance your farm’s productivity and sustainability.
Whether you choose vertical tillage or conventional plowing, it’s essential to implement best management practices to optimize soil health and crop performance. Regular soil testing, crop rotation, and residue management are crucial components of a successful tillage strategy. By staying informed and adapting to changing conditions, you can ensure the long-term success of your farming operation.